
Muscle biopsy: This can help detect or rule out a muscle disease.Analyzing this can help rule out other conditions. Spinal tap, or lumbar puncture: A doctor takes a sample of cerebrospinal fluid, which surrounds the brain and spinal cord.Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction study (NCS): An EMG measures the amount of electrical activity in muscles, while an NCS measures the speed at which electricity moves through muscles.MRI brain scan: An MRI cannot detect MND, but it can help rule out other conditions, such as a stroke, a brain tumor, or unusual brain structures.Blood and urine tests: These can help rule out other conditions and detect any rise in creatinine kinase, a substance that muscles produce when they break down.If a doctor suspects that someone has MND, they will refer them to a neurologist, who will take a medical history and do a thorough examination. The disease can become life threatening, and breathing problems are the most common cause of death.ĭoctors often find it difficult to diagnose MND in the early stages, as it can resemble other conditions, such as multiple sclerosis. Advanced stage signs and symptomsĮventually, a person with advanced ALS needs help moving, eating, breathing, or a combination of these. Some people also experience insomnia, anxiety, and depression. It also reports that around 12–15% of people with ALS develop dementia. changes in personality and emotional statesĪ 2017 study suggests that up to half of people with ALS experience brain involvement, including memory and language problems.uncontrollable yawning, which can lead to jaw pain.drooling, due to problems with swallowing.weight loss, as muscles lose their massĪs the condition progresses, the early symptoms become more severe.inappropriate emotional responses, such as laughing or crying.trouble breathing or shortness of breath.a weakening grip, which makes it hard to pick up and hold things.Typical symptoms begin in one of the following areas: The specific symptoms depend on the type of MND and the area of the body it affects.

In the early stage of MND, symptoms develop slowly and can resemble those of other health conditions. The diseases progress at different speeds and vary in severity. The different types of MND cause similar symptoms and have three stages: early, middle, and advanced. The long-term outlook depends on the type. It tends to affect the trunk, legs, and arms. There are three types, all caused by a genetic change known as SMA1.
It causes frequent choking spells and difficulty speaking, eating, and swallowing.

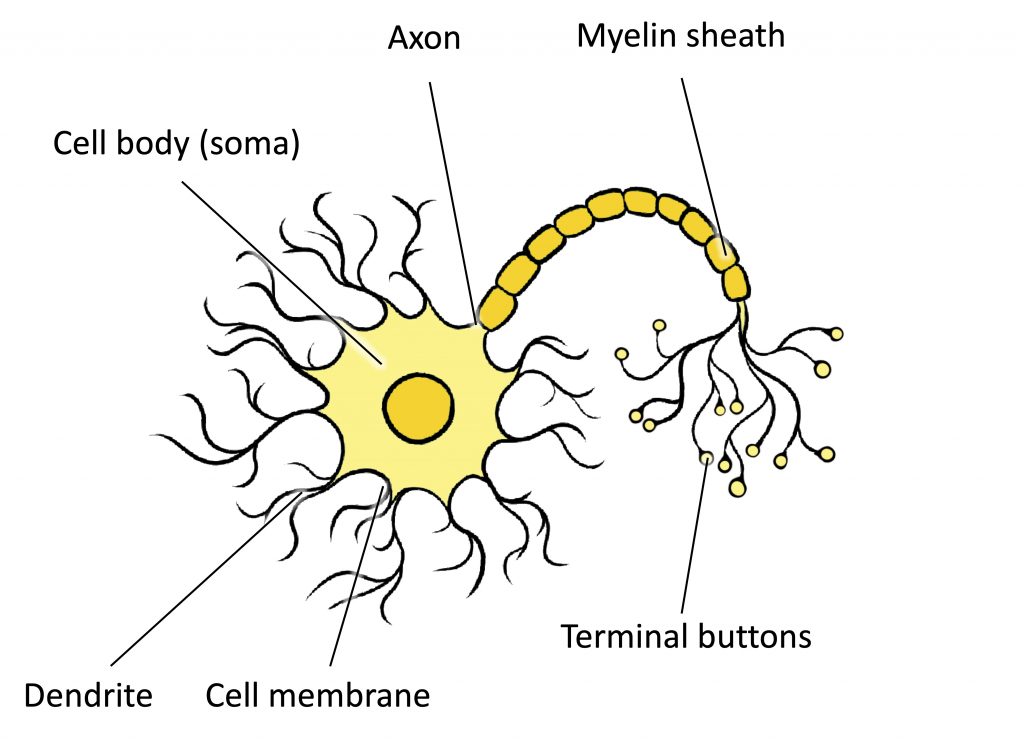
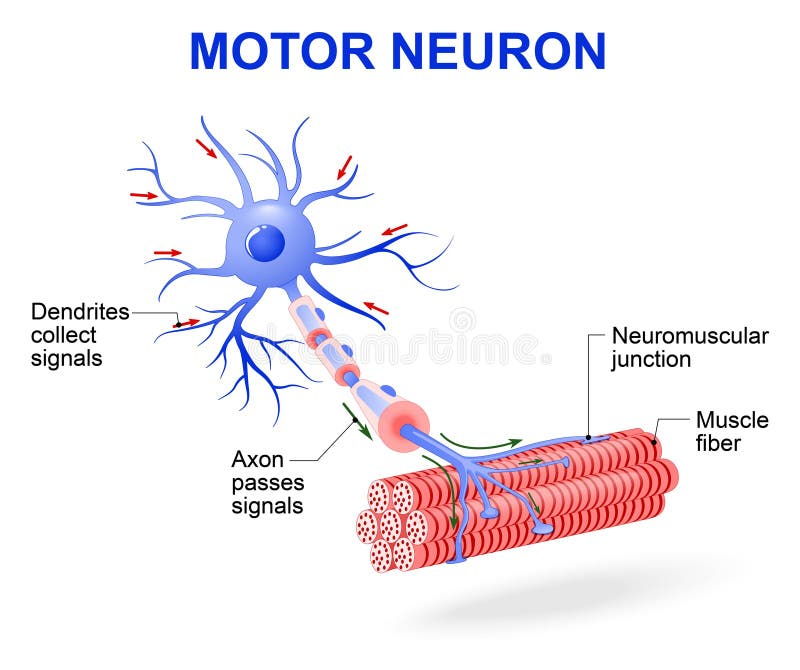
A spinal cord neuron stimulates a muscle to contract.Share on Pinterest funky-data/Getty Images.A neuron that takes taste information from your tongue and sends it to your brain.A neuron in the spinal cord receives touch information and then transmits that information to another spinal cord neuron that controls the movement of an arm muscle.For each type of neuron below, identify whether it is a sensory neuron, motor neuron, or interneuron.Compare and contrast sensory and motor neurons.Relate neurons to different types of nervous tissues.What is the potential for neurogenesis in the human brain? How does their arrangement allow nerve impulses to travel very rapidly along axons? Describe the myelin sheath and nodes of Ranvier.Identify the three main parts of a neuron and their functions.Interneurons carry nerve impulses back and forth often between sensory and motor neurons within the spinal cord or brain.They change nerve signals into the activation of these structures. \), carry nerve impulses from the central nervous system to muscles and glands.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
